Quick Fire Emission Dataset (QFED): Difference between revisions
m Added TOC |
m Updated the QFED tag to qfed-1_0_b4 |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
These are checkout and build instructions for QFED. We presume that the user has an account and appropriate permissions on '''progress''' to check code out, and access to the NCCS machines (e.g., '''discover''') to run code. | These are checkout and build instructions for QFED. We presume that the user has an account and appropriate permissions on '''progress''' to check code out, and access to the NCCS machines (e.g., '''discover''') to run code. | ||
The name of the module in the cvs repository is '''QFED'''. Currently the name of the development tag is '''qfed- | The name of the module in the cvs repository is '''QFED'''. Currently the name of the development tag is '''qfed-1_0_b4'''. To checkout the QFED source into the directory ''qfed'', for example, use the following command | ||
% cvs -d $CVSROOT co -d ./qfed -r qfed- | % cvs -d $CVSROOT co -d ./qfed -r qfed-1_0_b4 QFED | ||
Once the code is checked out set the '''ESMADIR''' variable to point to the QFED top directory, e.g.: | Once the code is checked out set the '''ESMADIR''' variable to point to the QFED top directory, e.g.: | ||
Revision as of 05:05, 4 June 2010
This page to contains information regarding QFED, mostly for developers.
How to Check Out and Build the Code
These are checkout and build instructions for QFED. We presume that the user has an account and appropriate permissions on progress to check code out, and access to the NCCS machines (e.g., discover) to run code.
The name of the module in the cvs repository is QFED. Currently the name of the development tag is qfed-1_0_b4. To checkout the QFED source into the directory qfed, for example, use the following command
% cvs -d $CVSROOT co -d ./qfed -r qfed-1_0_b4 QFED
Once the code is checked out set the ESMADIR variable to point to the QFED top directory, e.g.:
% setenv ESMADIR ${HOME}/projects/qfed
Make sure that you have a valid ${BASEDIR}. QFED code is known to compile against Baselibs-v3.1.7.
To build the code navigate to the source directory where you will find the main GNUMakefile:
% cd ./qfed/src
The available options can be seen by running gmake or gmake esma_help:
% gmake esma_help
Standard ESMA targets:
% make esma_install (builds and install under ESMADIR)
% make esma_clean (removes deliverables: *.[aox], etc)
% make esma_distclean (leaves in the same state as cvs co)
% make esma_doc (generates PDF, installs under ESMADIR)
% make esma_help (this message)
Environment:
ESMADIR = ...qfed/src/
BASEDIR = /opt/Baselibs/v3.1.7/
ARCH = Linux
SITE = hostname
To build and install QFED :
% make esma_install
followed by
% make PYTHON_INSTALL=python_install install
if you wish to install the python modules and scripts as well.
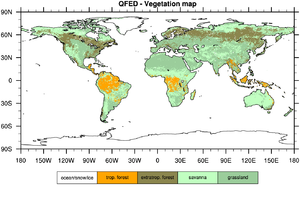
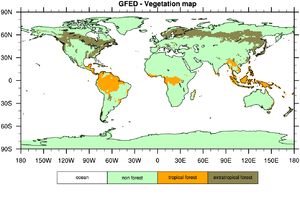
QFED Vegetation Map
The QFED vegetation classes are Tropical Forest, Extratropical Forest, Savanna and Grassland. The QFED vegetation map is derived from the global IGBP land cover data set by aggregating one or more IGBP classes into a single QFED class. QFED Tropical Forest corresponds to IGBP Evergreen Broadleaf for latitudes (30°S, 30°N), whereas QFED Extratropical Forest includes the rest of the IGBP forest types and IGBP Evergreen Broadleaf for latitudes outside the (30°S, 30°N) zone. All IGBP shrubland and savanna classes are aggregated into QFED Savanna class. Similarly, all IGBP grassland and cropland classes are agregated into the QFED Grassland class.
The QFED vegetation map uses the following numerical values for the vegetation classes:
Tropical Forest = 1 Extratropical Forest = 2 Savanna = 3 Grassland = 4
 |
 |