GEOS-5 AGCM Overview: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
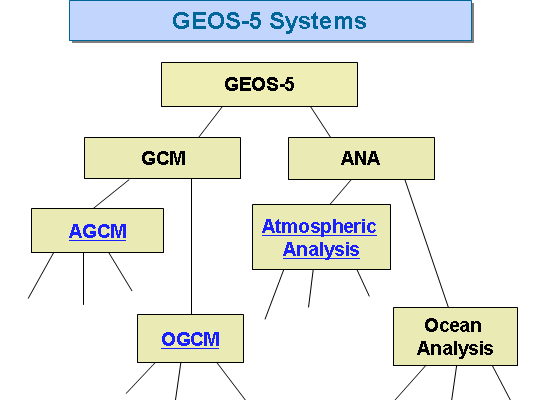
The Goddard Earth Observing System Model, Version 5 (GEOS-5) is a system of models integrated using the Earth System Modeling Framework ([http://www.esmf.ucar.edu ESMF]). The GEOS-5 DAS integrates the GEOS-5 AGCM with the Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation (GSI) atmospheric analysis developed jointly with NOAA/NCEP/EMC. The GEOS-5 systems are being developed in the GMAO to support NASA's earth science research in data analysis, observing system modeling and design, climate and weather prediction, and basic research. | The Goddard Earth Observing System Model, Version 5 (GEOS-5) is a system of models integrated using the Earth System Modeling Framework ([http://www.esmf.ucar.edu ESMF]). The GEOS-5 DAS integrates the GEOS-5 AGCM with the Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation (GSI) atmospheric analysis developed jointly with NOAA/NCEP/EMC. The GEOS-5 systems are being developed in the GMAO to support NASA's earth science research in data analysis, observing system modeling and design, climate and weather prediction, and basic research. | ||
<center> | |||
<center>[[Image:GEOS5_structure.gif]]</center> | |||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
desc none | desc none | ||
</imagemap> | </imagemap> | ||
<center>''GEOS-5 is supported by NASA's Modeling Analysis and Prediction (MAP) Program.''</center> | |||
Revision as of 07:48, 11 June 2008
The Goddard Earth Observing System Model, Version 5 (GEOS-5) is a system of models integrated using the Earth System Modeling Framework (ESMF). The GEOS-5 DAS integrates the GEOS-5 AGCM with the Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation (GSI) atmospheric analysis developed jointly with NOAA/NCEP/EMC. The GEOS-5 systems are being developed in the GMAO to support NASA's earth science research in data analysis, observing system modeling and design, climate and weather prediction, and basic research.
Error: Invalid title in link at line 3.